Stress is an inevitable part of life. Sometimes, it can motivate you to meet a deadline or push through a tough situation. But when stress becomes chronic, it doesn’t just stay in your mind—it manifests throughout your body. You might not realize it, but those nagging aches, headaches, or even digestive issues could be your body’s way of screaming, “Hey, slow down!”
1. Tense Muscles: Carrying Stress in Your Body
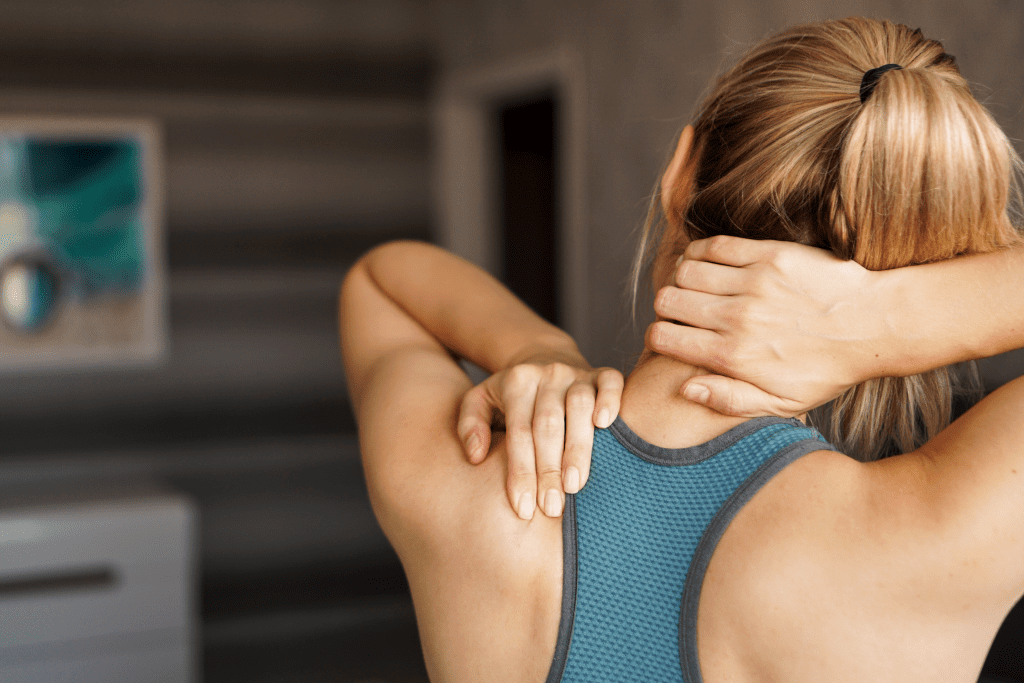

Have you ever caught yourself clenching your jaw or hunching your shoulders without even realizing it? That’s your body holding onto stress. Muscle tension is one of the most common physical signs of stress. It usually shows up in your neck, shoulders, and back, but it can affect any muscle group.
Why Does Stress Cause Muscle Tension?
When your body senses stress, it activates the fight-or-flight response, which causes muscles to tighten in preparation for action. If you’re constantly stressed, this tension becomes chronic, leading to discomfort, pain, or even tension headaches. Over time, you might develop stiffness or long-term muscle pain.
Video:
This is why anxiety gives you SO many strange symptoms
How to Loosen Up:
- Stretch regularly: Incorporate gentle stretches into your daily routine, especially if you sit for long periods.
- Try yoga or tai chi: These practices promote relaxation and flexibility.
- Massage therapy: A professional massage can release built-up tension.
- Heat therapy: Use warm showers or heating pads to soothe tight muscles.
2. Headaches: The Pressure in Your Head
Stress headaches are like wearing a too-tight headband that just won’t let up. They feel like a dull, aching pain around your forehead or the back of your neck. Sometimes, stress can also trigger migraines, making the pain more intense and throbbing.
Why Do You Get Stress Headaches?
When stress hormones spike, they can cause the muscles around your scalp and neck to tense up. This results in tension-type headaches that can last for hours or even days. If you already deal with migraines, stress can worsen their frequency and severity.
How to Ease the Pain:
- Stay hydrated: Dehydration can make headaches worse.
- Take breaks: Step away from screens to rest your eyes and mind.
- Practice relaxation techniques: Deep breathing or meditation can help reduce headache intensity.
- Avoid caffeine overload: Too much coffee can trigger or worsen headaches.
3. Digestive Issues: When Stress Hits Your Gut
Have you ever felt your stomach twist into knots before a big presentation? That’s your gut reacting to stress. But when stress is ongoing, it can wreak havoc on your digestive system. You might experience bloating, constipation, diarrhea, or acid reflux.
Why Does Stress Affect Digestion?
The gut-brain connection is powerful. When your brain senses stress, it sends signals to your digestive system, slowing down or speeding up processes. This can lead to issues like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or chronic stomach discomfort.
How to Calm Your Gut:
- Eat fiber-rich foods: Whole grains, vegetables, and fruits support healthy digestion.
- Limit trigger foods: Reduce caffeine, alcohol, and processed foods that irritate the gut.
- Practice mindful eating: Chew slowly and avoid eating while stressed.
- Hydrate: Water helps move food through your system efficiently.
4. Heart Palpitations: When Stress Affects Your Heartbeat
Ever feel your heart pounding for no apparent reason? Stress can cause heart palpitations, making it feel like your heart is racing or skipping beats. It’s a scary sensation, but usually harmless if it happens occasionally.
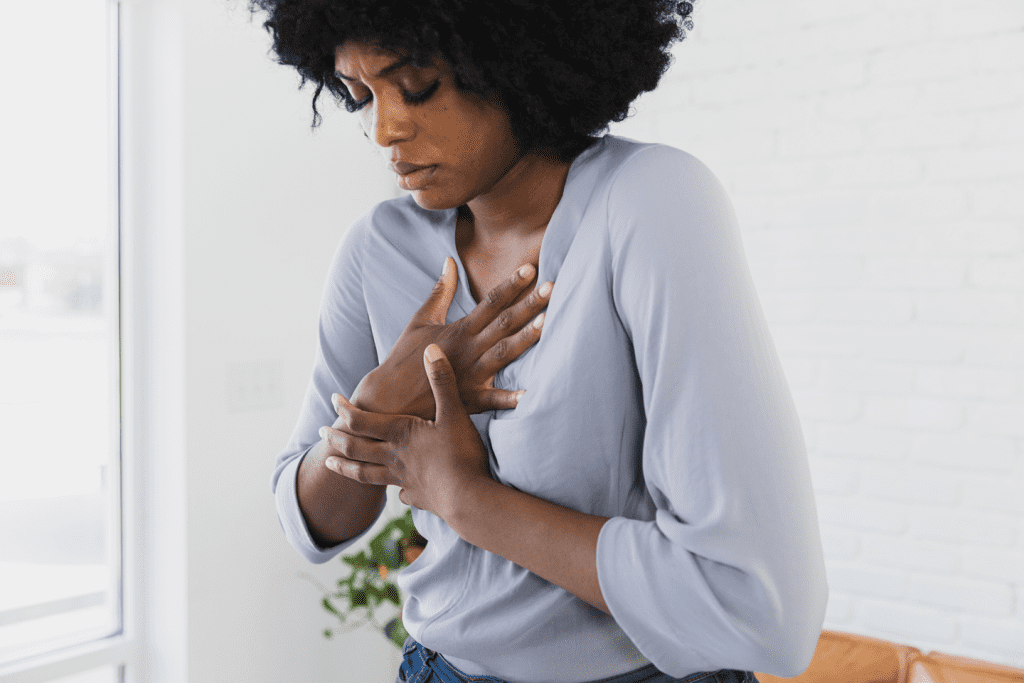

Why Does Stress Cause Heart Palpitations?
When stressed, your body releases adrenaline, which speeds up your heart rate. While this response prepares you for danger, chronic stress keeps your heart working overtime. Over time, this strain can contribute to high blood pressure and cardiovascular issues.
How to Steady Your Heartbeat:
- Cut back on stimulants: Reduce caffeine and alcohol intake.
- Deep breathing: Practice inhaling slowly through your nose and exhaling through your mouth.
- Regular exercise: Physical activity helps regulate heart rhythm and reduces anxiety.
- Stay grounded: Use grounding techniques, like focusing on your breathing or squeezing a stress ball.
5. Sleep Problems: Stress and Insomnia

Have you ever laid in bed with your mind racing, unable to sleep? Stress can cause insomnia by increasing cortisol levels, which keeps you alert instead of relaxed. Even if you manage to fall asleep, stress can cause frequent waking or restless sleep.
Why Does Stress Disrupt Sleep?
Your brain struggles to shut down when it’s processing worries or unfinished tasks. Elevated cortisol and adrenaline make your body think it needs to stay on high alert, making it difficult to wind down.
How to Get Better Sleep:
- Create a bedtime routine: Wind down with calming activities like reading or listening to soothing music.
- Limit screen time: The blue light from screens interferes with melatonin production.
- Practice relaxation: Try journaling or meditative breathing before bed.
- Skip late-night caffeine: Stimulants can keep you wired.
Video:
7 Signs of A Mental Breakdown
6. Irregular or Missed Periods: Stress and Hormonal Imbalance
Stress can throw your hormones off balance, leading to irregular periods or even missed cycles. It can also worsen PMS symptoms and cause more intense cramps.
Why Does Stress Affect Your Menstrual Cycle?
The hypothalamus, which regulates hormones, can become disrupted by chronic stress. As cortisol levels rise, they can interfere with the production of estrogen and progesterone, essential for maintaining a regular cycle.
How to Balance Your Cycle:
- Stay active: Moderate exercise helps regulate hormones.
- Eat nutrient-rich foods: Include leafy greens, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Reduce stress: Engage in hobbies that make you happy.
- Practice self-care: Take time to unwind and prioritize rest.
7. Weight Gain: Stress and Emotional Eating
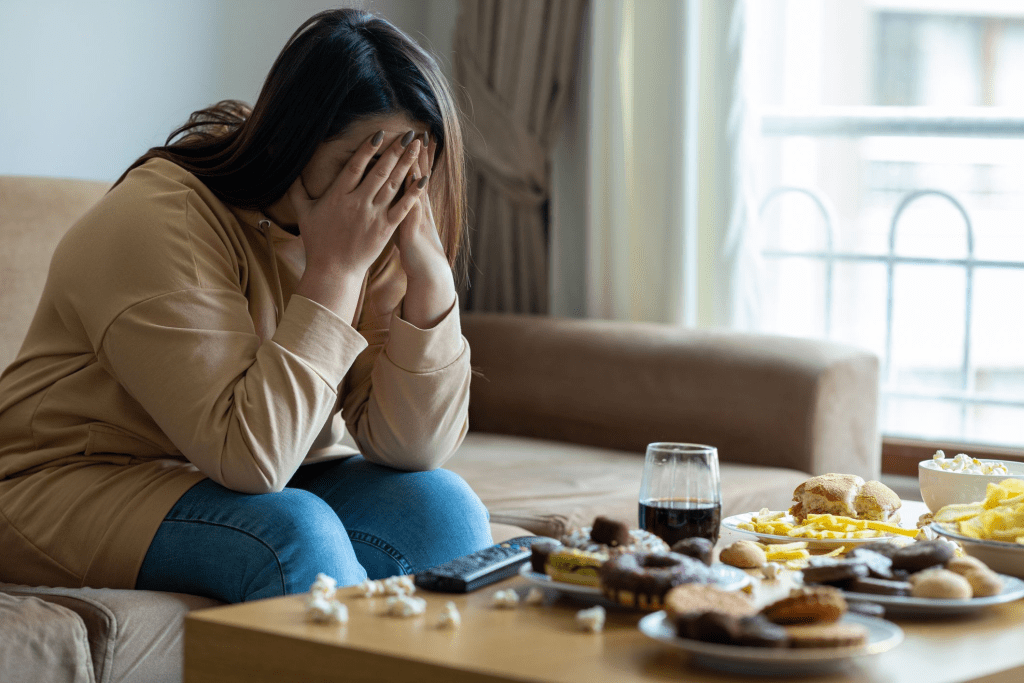

When stress strikes, many of us reach for comfort foods. Stress increases cortisol, which triggers cravings for sugar and high-calorie foods. Over time, this can lead to weight gain, particularly around the belly.
Why Does Stress Cause Weight Gain?
Stress hormones make your body think it needs to store energy, leading to fat accumulation. Emotional eating becomes a coping mechanism, but it ultimately worsens the problem.
How to Combat Stress Eating:
- Plan your meals: Have healthy snacks on hand.
- Mindful eating: Pay attention to your food and eat slowly.
- Stress-relieving activities: Replace eating with hobbies or exercise.
- Stay active: Regular physical activity reduces cortisol levels.
Conclusion
Stress impacts both your body and mind in more ways than you might think. From tense muscles to sleep issues, these symptoms can disrupt your quality of life. By identifying these signs early and taking proactive steps to manage stress, you can maintain better overall health.
Start with small changes—whether it’s practicing deep breathing, eating healthier, or setting aside time to relax. Your body will thank you for it. Remember, managing stress is not just about surviving—it’s about thriving!